HTTP 读写超时
服务端超时
对于暴露在互联网上的 HTTP 服务器来说,强制客户端连接超时非常重要。
非常慢或消息的客户端可能会导致文件描述符泄露,出现以下错误:
|
|
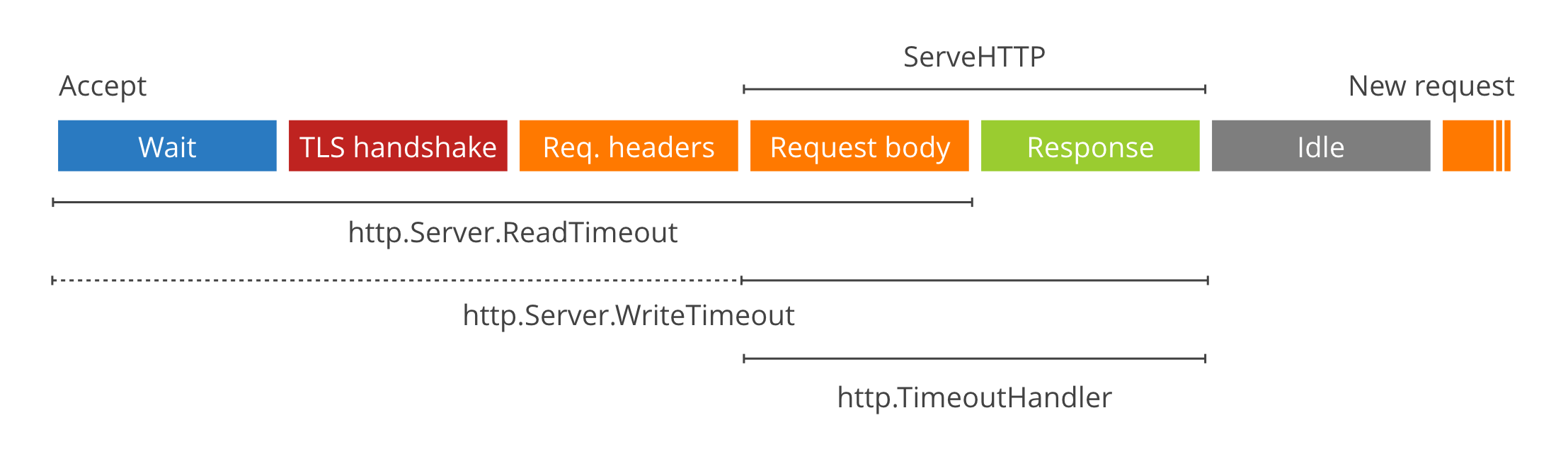
ReadTimeout 涵盖从接受连接到完全读取请求正文(如果您确实读取了正文,否则到标头末尾)的时间。它是通过在 Accept 之后立即调用 SetReadDeadline 在 net/http 中实现的。
WriteTimeout 通常通过在 readRequest 末尾调用 SetWriteDeadline 来覆盖从请求标头读取结束到响应写入结束的时间(也称为 ServeHTTP 的生命周期)。
http.TimeoutHandler 。它不是服务器参数,而是限制 ServeHTTP 调用最大持续时间的 Handler 包装器。它的工作原理是缓冲响应,并在超过截止时间时发送 504 网关超时。
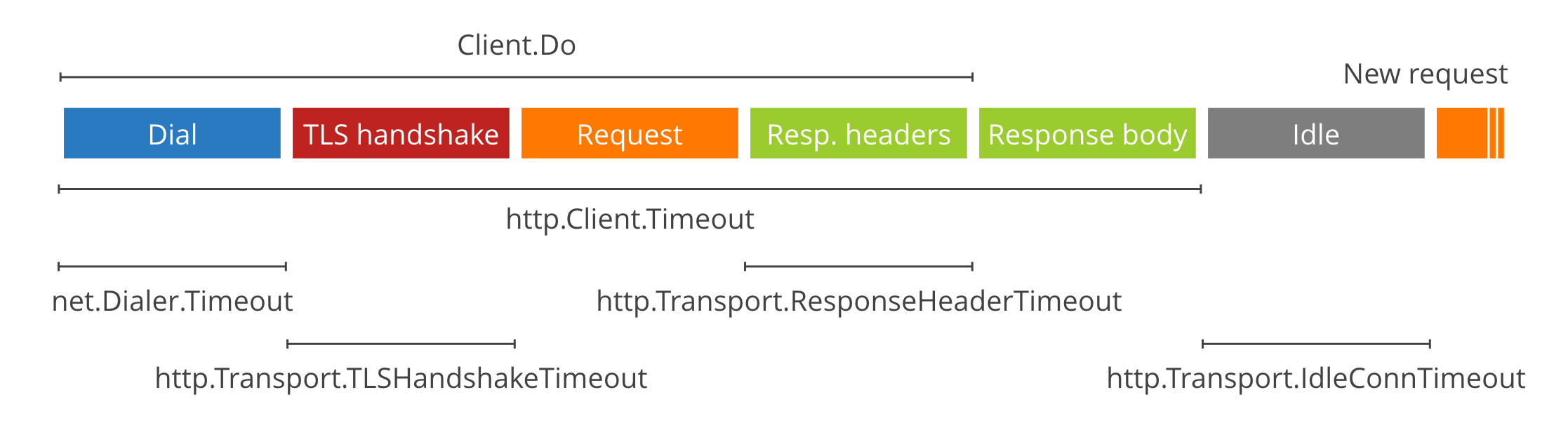
客户端超时
最容易使用的是 http.Client 的 Timeout 字段。它涵盖了整个流程。
http.Get 等包级函数使用没有超时的客户端,因此在开放的 Internet 上使用是危险的。
net.Dialer.Timeout限制建立 TCP 连接所花费的时间(如果需要新连接)http.Transport.TLSHandshakeTimeout限制执行 TLS 握手所花费的时间。http.Transport.ResponseHeaderTimeout限制读取响应标头所花费的时间。
|
|
如上面代码所示,可以使用 http.Server 定义读写超时时间,通常在 5~30 秒之间,这有助于防止应用程序无限期地阻塞在HTTP响应的读取或写入操作上,从而导致应用程序失去响应并影响整体性能。
ReadTimeout 是从 accept 到 request.Body 被完全读取的时间,如果不读 body 则时间截止到读完 header 为止。
WriteTimeout 是从 request header 的读取结束开始,到 response write 结束为止。
使用以上定义的代码,在上传文件功能中,如果文件的大小不确定,大文件读取用时超过预定义的 ReadTimeout,则会出现超时错误,类似于 read tcp [::1]:1133->[::1]:57471: i/o timeout。
在 Go 1.20 中新增加了 http.ResponseController 类型,使用该包可以单独控制每个 Handler 的读写超时时间。
参考 Github issue net/http: ResponseController to manipulate per-request timeouts (and other behaviors) #54136。
它有以下优点:
- 根据每个请求设置读写超时时间。
- http.Flusher 和 http.Hijacker 使用更轻松。
- 使创建和使用自定义的 http.ResponseWrite 实现变得更容易和更安全。
使用
|
|